MNIST dataset
13 Jan 2018
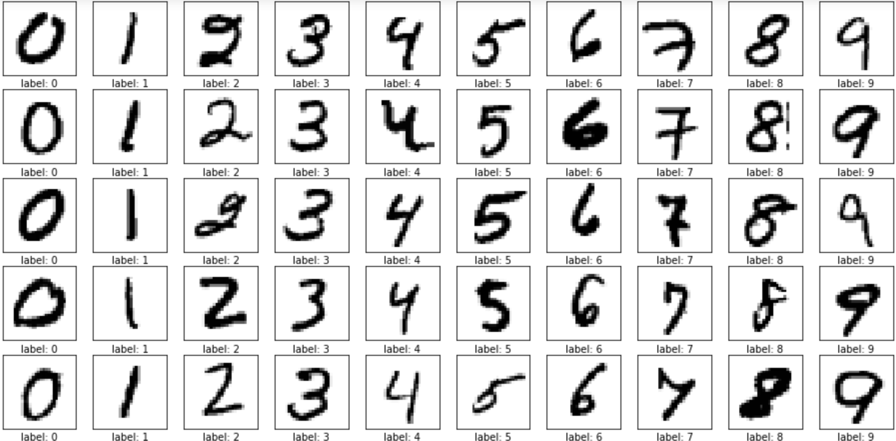
MNIST is a dataset of 60.000 examples of handwritten digits. It is a good database to check models of machine learning.
All images are a greyscale of 28x28 pixels.
LeCun began to test this dataset in 1998 with 12% error (linear classifier). Last models have reach a 0.5% error.
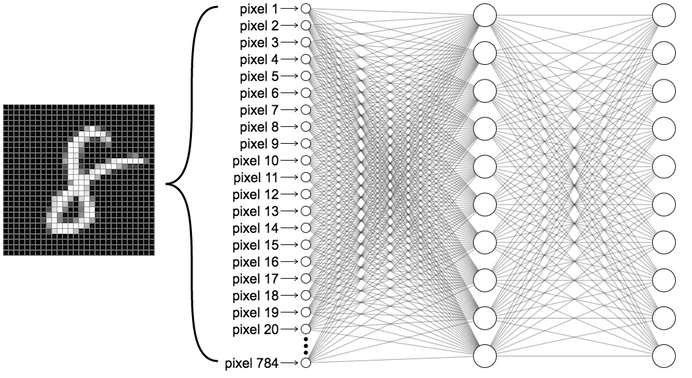
Example coded in Keras (using tesorflow backend).
- Input layer 28*28 = 784
- First layer: Dense 512, activation: relu
- Second layer: Dense 512, activation: relu
- Final layer: Dense 10, activation: softmax
- Function loss: cross entropy
- Gradient algoritm: Minibatch 128 size and RMSprop
- Num epochs: 20
'''Trains a simple deep NN on the MNIST dataset.
Gets to 98.40% test accuracy after 20 epochs
(there is *a lot* of margin for parameter tuning).
2 seconds per epoch on a K520 GPU.
'''
from __future__ import print_function
import keras
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
batch_size = 128
num_classes = 10
epochs = 20
# the data, shuffled and split between train and test sets
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.reshape(60000, 784)
x_test = x_test.reshape(10000, 784)
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')
x_train /= 255
x_test /= 255
print(x_train.shape[0], 'train samples')
print(x_test.shape[0], 'test samples')
# convert class vectors to binary class matrices
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.summary()
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer=RMSprop(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
Example in pytorch:
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.autograd import Variable
# Training settings
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Example')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='number of epochs to train (default: 10)')
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.01, metavar='LR',
help='learning rate (default: 0.01)')
parser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.5, metavar='M',
help='SGD momentum (default: 0.5)')
parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='disables CUDA training')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
help='random seed (default: 1)')
parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
args = parser.parse_args()
args.cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
if args.cuda:
torch.cuda.manual_seed(args.seed)
kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True} if args.cuda else {}
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../data', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x)
model = Net()
if args.cuda:
model.cuda()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum)
def train(epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
if args.cuda:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
data, target = Variable(data), Variable(target)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.data[0]))
def test():
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
for data, target in test_loader:
if args.cuda:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
data, target = Variable(data, volatile=True), Variable(target)
output = model(data)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, size_average=False).data[0] # sum up batch loss
pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1] # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred)).cpu().sum()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
train(epoch)
test()
Tensorflow example:
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
"""Convolutional Neural Network Estimator for MNIST, built with tf.layers."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
def cnn_model_fn(features, labels, mode):
"""Model function for CNN."""
# Input Layer
# Reshape X to 4-D tensor: [batch_size, width, height, channels]
# MNIST images are 28x28 pixels, and have one color channel
input_layer = tf.reshape(features["x"], [-1, 28, 28, 1])
# Convolutional Layer #1
# Computes 32 features using a 5x5 filter with ReLU activation.
# Padding is added to preserve width and height.
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 28, 28, 1]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 28, 28, 32]
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=input_layer,
filters=32,
kernel_size=[5, 5],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Pooling Layer #1
# First max pooling layer with a 2x2 filter and stride of 2
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 28, 28, 32]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 14, 14, 32]
pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2)
# Convolutional Layer #2
# Computes 64 features using a 5x5 filter.
# Padding is added to preserve width and height.
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 14, 14, 32]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 14, 14, 64]
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool1,
filters=64,
kernel_size=[5, 5],
padding="same",
activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Pooling Layer #2
# Second max pooling layer with a 2x2 filter and stride of 2
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 14, 14, 64]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 7, 7, 64]
pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv2, pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2)
# Flatten tensor into a batch of vectors
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 7, 7, 64]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 7 * 7 * 64]
pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
# Dense Layer
# Densely connected layer with 1024 neurons
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 7 * 7 * 64]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 1024]
dense = tf.layers.dense(inputs=pool2_flat, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# Add dropout operation; 0.6 probability that element will be kept
dropout = tf.layers.dropout(
inputs=dense, rate=0.4, training=mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
# Logits layer
# Input Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 1024]
# Output Tensor Shape: [batch_size, 10]
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dropout, units=10)
predictions = {
# Generate predictions (for PREDICT and EVAL mode)
"classes": tf.argmax(input=logits, axis=1),
# Add `softmax_tensor` to the graph. It is used for PREDICT and by the
# `logging_hook`.
"probabilities": tf.nn.softmax(logits, name="softmax_tensor")
}
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode=mode, predictions=predictions)
# Calculate Loss (for both TRAIN and EVAL modes)
onehot_labels = tf.one_hot(indices=tf.cast(labels, tf.int32), depth=10)
loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(
onehot_labels=onehot_labels, logits=logits)
# Configure the Training Op (for TRAIN mode)
if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(
loss=loss,
global_step=tf.train.get_global_step())
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode=mode, loss=loss, train_op=train_op)
# Add evaluation metrics (for EVAL mode)
eval_metric_ops = {
"accuracy": tf.metrics.accuracy(
labels=labels, predictions=predictions["classes"])}
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode, loss=loss, eval_metric_ops=eval_metric_ops)
def main(unused_argv):
# Load training and eval data
mnist = tf.contrib.learn.datasets.load_dataset("mnist")
train_data = mnist.train.images # Returns np.array
train_labels = np.asarray(mnist.train.labels, dtype=np.int32)
eval_data = mnist.test.images # Returns np.array
eval_labels = np.asarray(mnist.test.labels, dtype=np.int32)
# Create the Estimator
mnist_classifier = tf.estimator.Estimator(
model_fn=cnn_model_fn, model_dir="/tmp/mnist_convnet_model")
# Set up logging for predictions
# Log the values in the "Softmax" tensor with label "probabilities"
tensors_to_log = {"probabilities": "softmax_tensor"}
logging_hook = tf.train.LoggingTensorHook(
tensors=tensors_to_log, every_n_iter=50)
# Train the model
train_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={"x": train_data},
y=train_labels,
batch_size=100,
num_epochs=None,
shuffle=True)
mnist_classifier.train(
input_fn=train_input_fn,
steps=20000,
hooks=[logging_hook])
# Evaluate the model and print results
eval_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
x={"x": eval_data},
y=eval_labels,
num_epochs=1,
shuffle=False)
eval_results = mnist_classifier.evaluate(input_fn=eval_input_fn)
print(eval_results)
if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run()